55512N5551 2N-5551 Transistor 180V 0.6mA NPN Transistor TO-92 Bipolar Transistor BJT NPN General Purpose Amplifier 3 Pin Leads Transistor
This article explains 2N5551 transistor pinout, equivalent, uses, features, explanation, where and how to use this transistor and what to do to make this transistor perform long term in an electronic circuit.
Pin Configuration:
Technical specifications:
- Package Type: TO-92
- Transistor Type: NPN
- Max Collector Current(IC):0. 6A or 600mA
- Max Collector-Emitter Voltage (VCE): 160V
- Max Collector-Base Voltage (VCB): 180V
- Max Emitter-Base Voltage (VBE): 6V
- Max Collector Dissipation (Pc): 625 mW
- Max Transition Frequency (fT): 100 MHz
- Minimum & Maximum DC Current Gain (hFE): 80 – 250
- Max Storage & Operating temperature Should be: -55 to +150 Centigrade
Features:
- Amplifier NPN Transistor
- High DC Current Gain (hFE), typically 80 when IC=10mA
- Continuous Collector current (IC) is 600mA
- Collector-Emitter voltage (VCE) is 160 V
- Collector-Base voltage (VCB) is 180V
- Emitter Base Voltage (VBE) is 6V
- Transition Frequency is 100MHz
- Available in To-92 Package
Alternative NPN Transistors:
BC549, BC636, BC639, BC547, 2N2369, 2N3055, 2N3904, 2N3906, 2SC5200
2N5551 Equivalent Transistors:
NTE194, 2N5833, 2N5088, 2N3055, 2N5401 (PNP)
Same Family Transistors:
2N5550
Where to use 2N5551:
The 2N5551 is an NPN amplifier Transistor with an amplification factor (hfe) of 80 when the collector current is 10mA. It also has decent switching characteristics (Transition frequency is 100MHz) hence can amplify low-level signals.
Due to this feature, the transistor is commonly used for amplification of audio or other low power signals. So if you are looking for an NPN transistor for you amplifier circuit then this transistor might be the right choice.
How to use 2N5551:
As told earlier the 2N5551 NPN transistor is widely used for amplification. A very simple bare minimum circuit for a transistor to work as an amplifier is shown below. The simulation graph that shows the amplified output sine wave can also be found.
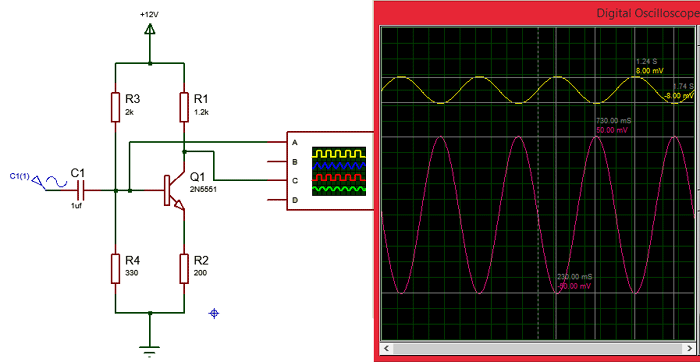
Here the input sine wave of magnitude 8mV (yellow colour) is amplified to 50mV (Pink colour) as shown in the graph. In the above circuit the resistors R3 and R4 form a potential divider which decides the Emitter -Base voltage (VBE). The Resistor R1 is the load resistor and the resistor R2 is the emitter resistor. Changing the value of RL will affect the amplification of the output wave.
A transistor is normally a current amplifier, meaning the current flowing though the base will be amplified in the current flowing through the collector. This amplification depends on the amplification factor (hfe) which is 80 for 2N5551. This means that the collector current will be amplified by 80 times than that of the base current.
I = βI
Another current that we have bring into consideration is the emitter current (IE), but due to transistor action we assume that Emitter current is almost equal to the value of Collector current, however the difference between the both can be found with the value of α. Normally the value of collector current will e given by
I = I + I
The output is obtained across the collector which is the Collector-Emitter voltage (VCE). This output voltage depends on the Input voltage (Vcc, here 12V) without the voltage drop across the loads resistor (R1). Therefore the output voltage Vout can be given as
Vout = VCE = (Vcc – IcRc)
Applications:
- Low power amplifiers
- Current amplifiers
- Small signal boosters
- Audio or other signal amplifiers
- Darlington pair
- Package Type: TO-92
- Transistor Type: NPN
- Max Collector Current(IC):0. 6A or 600mA
- Max Collector-Emitter Voltage (VCE): 160V
- Max Collector-Base Voltage (VCB): 180V
- Max Emitter-Base Voltage (VBE): 6V
- Max Collector Dissipation (Pc): 625 mW
- Max Transition Frequency (fT): 100 MHz
- Minimum & Maximum DC Current Gain (hFE): 80 – 250
Login to ask a question
 Global Finds
Global Finds  Quick Commerce
Quick Commerce  Grocery
Grocery  Electronics & Appliances
Electronics & Appliances  Mother, Baby & Toys
Mother, Baby & Toys _20.png) Beauty
Beauty  Sports
Sports  Automotive
Automotive  Stationery, Books & Music
Stationery, Books & Music _20.png) Fashion Luxe
Fashion Luxe  Daily Bazar
Daily Bazar _20.jpeg) Home
Home  Garden & Pet Care
Garden & Pet Care  Special Weekly Offer
Special Weekly Offer  Global Finds
Global Finds  Quick Commerce
Quick Commerce  Grocery
Grocery  Electronics & Appliances
Electronics & Appliances  Mother, Baby & Toys
Mother, Baby & Toys _20.png) Beauty
Beauty  Sports
Sports  Automotive
Automotive  Stationery, Books & Music
Stationery, Books & Music _20.png) Fashion Luxe
Fashion Luxe  Daily Bazar
Daily Bazar _20.jpeg) Home
Home  Garden & Pet Care
Garden & Pet Care  Special Weekly Offer
Special Weekly Offer 


