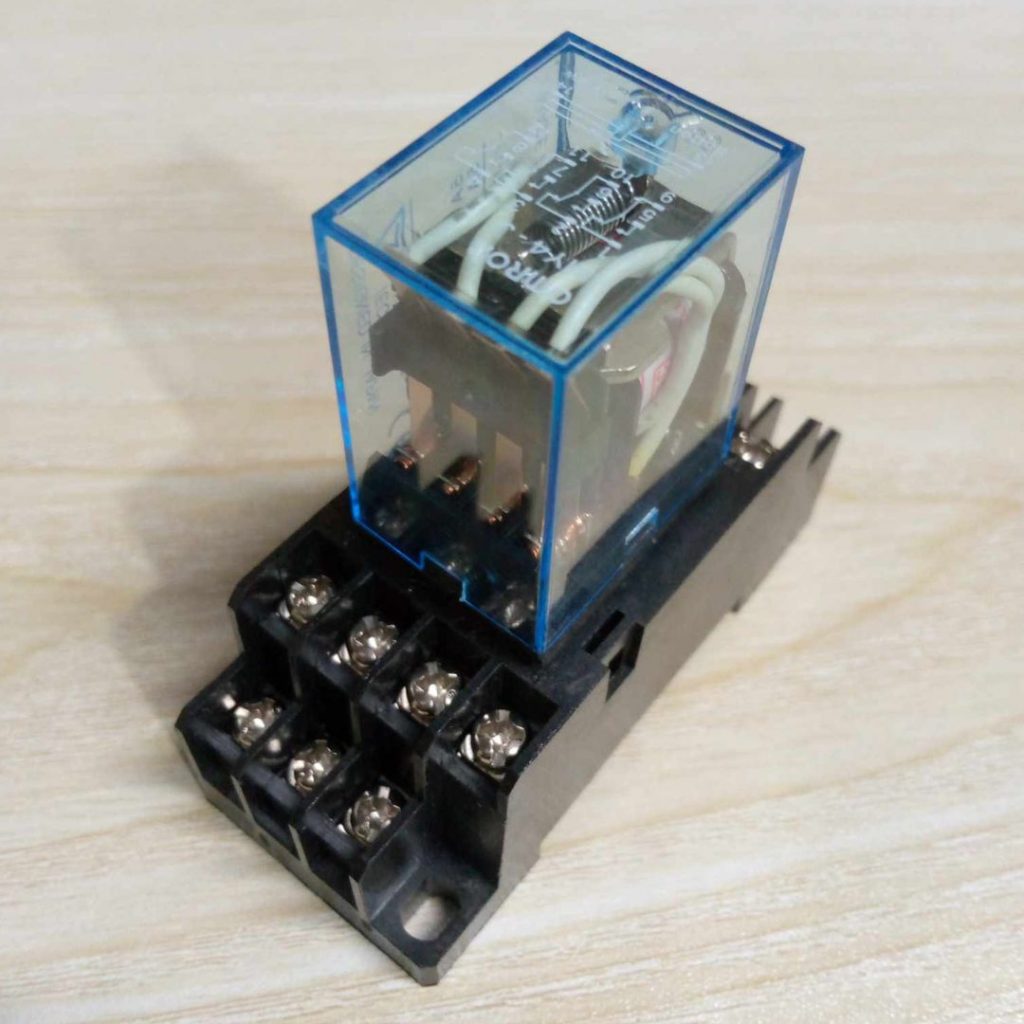
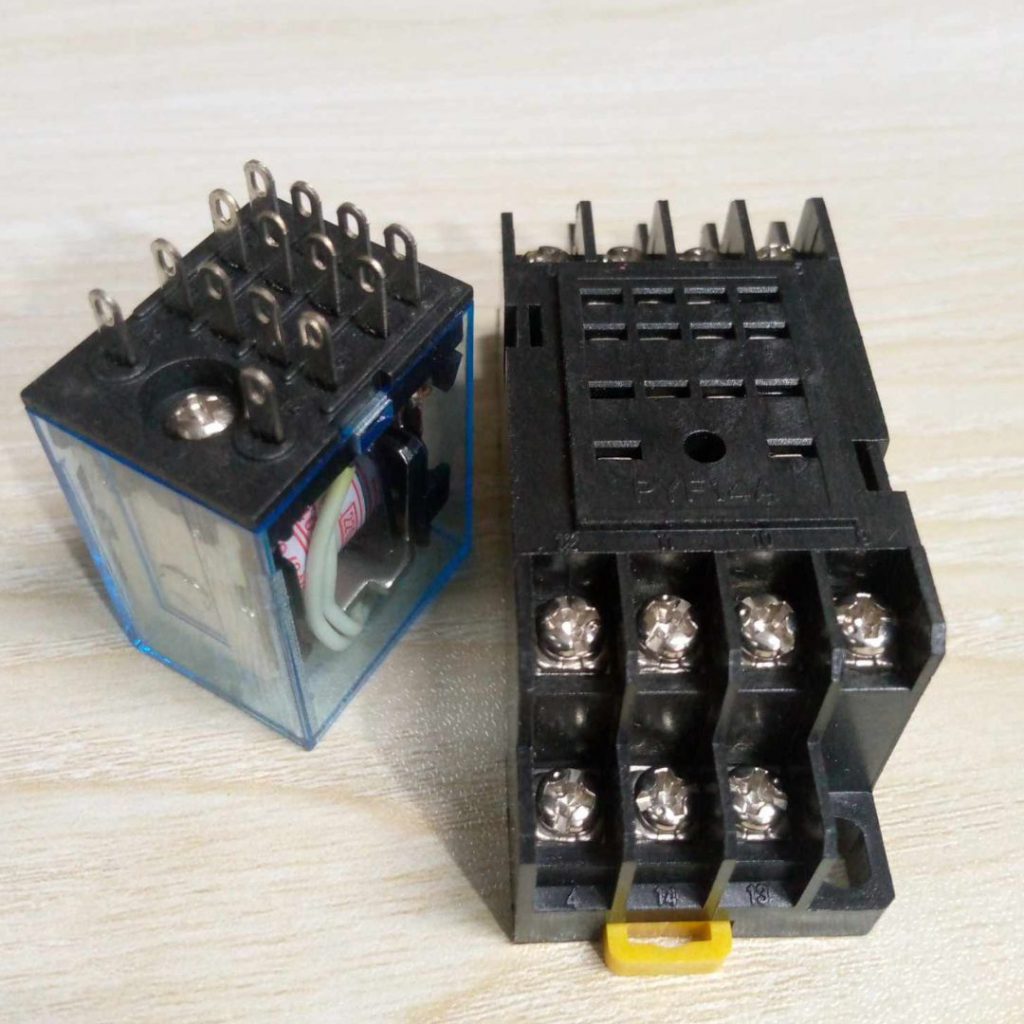
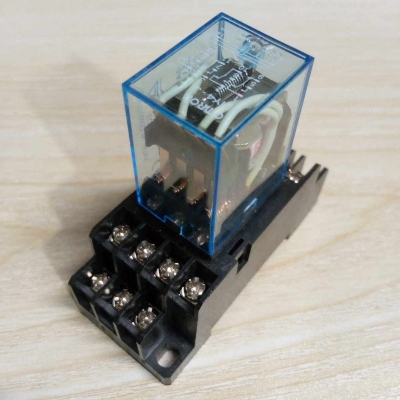
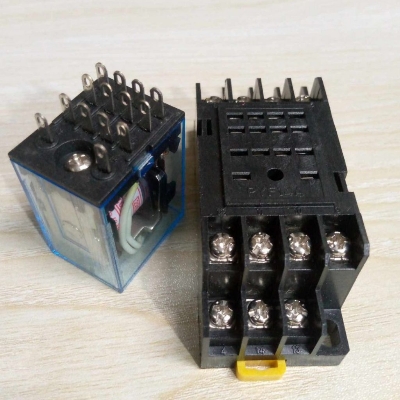
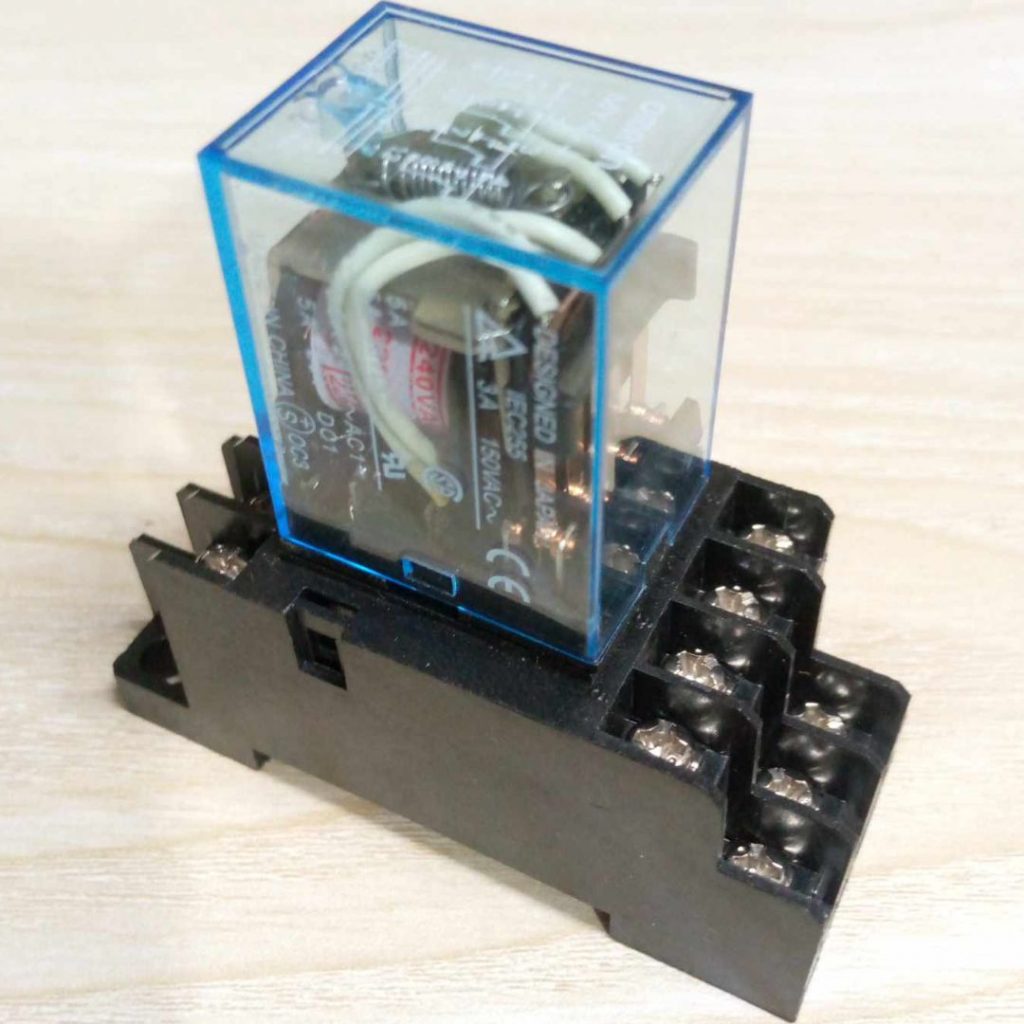
Description: AC 220V 14-Pin Electromagnetic Relay with PTF14A Socket Base
The AC 220V 14-Pin Electromagnetic Relay with PTF14A Socket Base is a type of electromagnetic relay used to control circuits with higher power and voltage, commonly found in industrial control systems, automation, or electrical devices. Here’s a breakdown of the components and details:
1. AC 220V Electromagnetic Relay:
- Voltage Rating: The relay is designed for 220V AC operation, meaning it can switch AC voltages of up to 220V.
- Electromagnetic Principle: Relays like these use an electromagnet to control a switching mechanism. When an electric current flows through the coil, it creates a magnetic field that attracts a movable contact, closing or opening the switch.
- Contact Configuration: Typically, these relays have a variety of contact configurations (SPDT, DPDT, etc.), with 14 pins, likely providing multiple contact sets for various uses.
- Load Rating: It can handle high-current applications, often used in power systems, motors, HVAC systems, or other electrical equipment that requires switching at high voltages.
- Coil Resistance & Power: The coil’s resistance is designed to work at 220V AC, and when energized, it consumes a specific power (measured in watts).
2. 14-Pin Relay:
- Number of Pins: The relay has 14 pins which likely include:
- Coil pins (2 pins): Used to energize the coil (creating a magnetic field).
- Common pin: The central point where contacts make connections.
- Normally Open (NO) & Normally Closed (NC) pins: These provide the switching functions that open or close the circuit, depending on the relay’s state.
- Other Pins for Multiple Contacts: Some relays may have additional pins to support multiple contact sets for complex switching requirements.
3. PTF14A Socket Base:
- The PTF14A socket is a type of relay base designed to hold the 14-pin relay.
- Compatibility: The PTF14A socket ensures that the relay is securely mounted and allows easy connection to external circuits.
- Wiring Interface: It makes the relay easy to install and replace in a system. The socket has the necessary connectors for the relay’s pins, typically designed for 14-pole connections.
- Type of Mounting: Usually, it is designed for DIN rail mounting, which is common in industrial applications, providing easy installation and removal.
4. Applications:
- Industrial Automation: Used in control panels, PLCs (Programmable Logic Controllers), or other systems where high-voltage AC signals need to be switched or controlled.
- Power Systems: Suitable for controlling power equipment like motors, fans, pumps, and HVAC systems.
- Home Appliances: Can be found in appliances like washing machines, refrigerators, or HVAC units where electromagnetic switching is needed.
5. Common Features:
- Durability: The relay is built to last in demanding environments, designed for frequent switching operations without significant wear.
- Electrical Isolation: The relay offers isolation between the low-voltage control side (coil) and the high-voltage load side (contacts).
- Temperature and Vibration Resistance: Typically rated to function within a certain range of temperature and vibration conditions.
6. Specifications:
- Coil Voltage: 220V AC (others can be available, but this is the most common for this type of relay).
- Contact Rating: Varies depending on the relay type, but it can typically handle current ratings up to 10A or higher.
- Switching Speed: Depends on the design, but usually in the range of milliseconds.
- Mounting: Base socket ensures easy installation and allows the relay to be securely mounted to a panel or a system.
- Coil Voltage: AC 220V ±10%
- Coil Frequency: 50/60 Hz
- Contact Form: 4PDT (4 Form C)
- Number of Pins: 14
- Contact Rating: 5A @ 250VAC / 30VDC (resistive load)
- Contact Material: Silver alloy
- Dielectric Strength: 2000VAC between coil and contacts
- Power Consumption: Approx. 1.2–1.5 VA (depending on model)
- Insulation Resistance: ≥100 MΩ at 500VDC
- Mechanical Life: 10 million operations (no load)
- Electrical Life: 100,000 operations (rated load)
- Operating Temperature: -25°C to +55°C
- Mounting Type: Plug-in via PTF14A Socket Base
- Socket Base Type: PTF14A (DIN rail or panel mountable)
- Indicators: Optional LED indicator and mechanical flag
- Protection: Optional RC snubber/diode (depends on model)
- Dimensions (Relay): Approx. 28 x 21.5 x 35 mm (W x D x H)
- Dimensions (Socket Base): Approx. 69 x 27 x 24 mm
Customer Questions and answers :
Login to ask a question

 Grocery
Grocery _20.png) Beauty
Beauty  Sports
Sports  Automotive
Automotive _20.png) Fashion Luxe
Fashion Luxe _20.jpeg) Home
Home  Mother, Baby & Toys
Mother, Baby & Toys  Special Weekly Offer
Special Weekly Offer  Stationery, Books & Music
Stationery, Books & Music  Garden & Pet Care
Garden & Pet Care  Grocery
Grocery _20.png) Beauty
Beauty  Sports
Sports  Automotive
Automotive _20.png) Fashion Luxe
Fashion Luxe _20.jpeg) Home
Home  Mother, Baby & Toys
Mother, Baby & Toys  Special Weekly Offer
Special Weekly Offer  Stationery, Books & Music
Stationery, Books & Music  Garden & Pet Care
Garden & Pet Care